Properties in ASP.NET Server Controls
Properties are similar to fields but have accessor methods. You should expose properties instead of public fields from your controls because properties allow data hiding, can be versioned, and are supported by visual designers such as Visual Studio .NET. The accessor functions can perform additional program logic in addition to setting or retrieving a property.
Properties Inherited from Control
The following list describes some of the commonly accessed properties.
- Controls — The collection of a control's child controls.
- ID — A user-supplied identifier for a control.
- Page — The page that contains the control.
- Parent — The control whose Controls collection a control belongs to. (Control A is a parent of control B if B is an element of A.Controls).
- ViewState — A data structure that is sent to the client and back and is generally used for persisting form data across round trips. ViewState is of type StateBag, which is a dictionary that stores data as name/value pairs.
- EnableViewState — Indicates whether a control maintains its view state across round trips. If a parent control does not maintain its view state, the view state for its child controls is automatically not maintained.
- UniqueID — The hierarchically-qualified unique identifier assigned to a control by the ASP.NET page framework.
- ClientID — A unique identifier assigned to a control by the ASP.NET page framework and rendered as the HTML ID attribute on the client. The ClientID is different from the UniqueID because the UniqueID can contain the colon character (:), which is not valid in the HTML ID attribute (and is not allowed in variable names in client-side script).
- Visible — Determines whether a control is visible on a page.
Properties Inherited from WebControl
- Font — The font for the control.
- ForeColor — The foreground color of the control.
- BackColor — The background color of the control.
- Height — The height of the control.
- Width — The width of the control.
- Attributes — A collection of name/value pairs rendered to the client as attributes. The Attributes property contains the union of declaratively set attributes that do not correspond to properties (or events) of the control and those that are set programmatically.
AutoPostBack Property
Autopostback is the mechanism, by which the page will be posted ,back to the server automatically based on some events in the web controls. In some of the web controls, the property called auto post back, which if set to true, will send the request to the server when an event happens in the control. If this property is set to TRUE the automatic post back is enabled, otherwise FALSE. Default value of AutoPostBack property is FALSE.
For Example
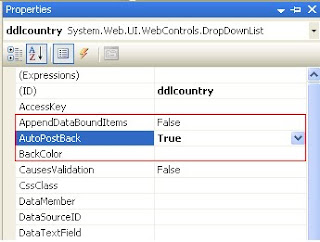
Why we need to set autopostback=true of controlsConsider a scenario where the web page is used for entering the user information. The page contains two dropdownlist controls ddlcountry and ddlstate. When user selects the country, the appropriate states be filled in the ddlstate which is loaded from the database. For achieving this requirement, we can set the autopostback property of ddlcountry to true. If we do that we can handle the event in the server side and write code to populate the ddlstate with the values from the database.
This is how we use the autopostback property.
No comments:
Post a Comment